What Is User Experience (UX) Design? The Ultimate Guide
User Experience, or UX design, focuses on how users interact with products, websites, or applications. It is all about creating meaningful and enjoyable experiences for people who use your product. From the first impression to the last click, UX design defines how intuitive, accessible, and satisfying a digital product feels.
In simple terms, UX design is about making technology feel human. When users can easily navigate a website, complete a task without frustration, or enjoy using a product, that is the result of good UX design.
Why UX Design Matters
In today’s digital world, design is more than just visuals. It is about how users think, feel, and behave when interacting with your product. A well-designed user experience can:
- Increase user satisfaction and trust
- Reduce friction and confusion
- Improve conversion rates and retention
- Strengthen brand reputation
Great UX design turns visitors into loyal users by focusing on usability, accessibility, and emotional connection.
Key Principles of UX Design
To create effective user experiences, designers rely on a few timeless principles that apply across industries and technologies.
1. User-Centered Design
At the heart of UX is understanding the user. Designers must research user needs, behaviors, and motivations to create solutions that truly serve them. This involves user interviews, surveys, and usability testing. The more you understand your audience, the better you can design for them.
2. Simplicity and Clarity
Good UX avoids unnecessary complexity. Users should not have to think too hard to complete an action. Every button, label, and layout element should serve a clear purpose. Simplicity reduces cognitive load and improves overall satisfaction.
3. Consistency
Consistency builds trust. Users feel comfortable when interface elements behave predictably. Fonts, colors, spacing, and interaction patterns should remain uniform across the product. This makes navigation easier and helps users learn your system faster.
4. Accessibility
Inclusive design ensures that everyone, including people with disabilities, can use your product. Accessibility involves readable text, proper color contrast, keyboard navigation, and support for assistive technologies. A product that everyone can use naturally performs better.
5. Feedback and Response
Every user action should trigger a clear response from the system. Whether it is a success message, a loading indicator, or an error alert, feedback helps users understand what is happening and reduces uncertainty.
6. Visual Hierarchy
A strong visual hierarchy guides users’ attention to what matters most. Designers use contrast, color, size, and placement to highlight key actions and information. When visual hierarchy is done right, users can scan and understand content effortlessly.
7. Usability Testing and Iteration
No design is perfect on the first try. Testing helps identify usability issues and improve the product based on real user feedback. Continuous iteration ensures that the design evolves as user needs and business goals change.
The UX Design Process
UX design is both creative and analytical. A typical UX workflow includes:
- Research – Understanding users, their goals, and pain points through interviews, analytics, and observation.
- Define – Synthesizing insights to create personas, user journeys, and clear problem statements.
- Ideate – Brainstorming and sketching possible solutions.
- Design – Creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes that bring ideas to life.
- Test – Conducting usability tests to evaluate design effectiveness.
- Implement and Refine – Collaborating with developers to launch and improve the final product.
This process is iterative, meaning designers continuously learn and refine as the product grows.
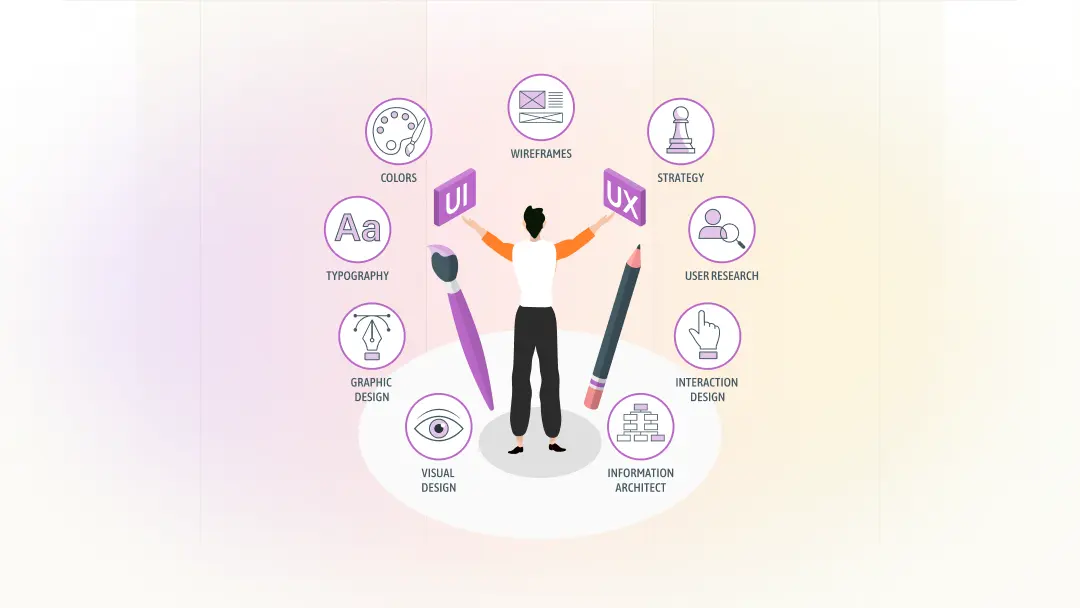
Skill Requirements for Becoming a User Experience Designer
The demand for skilled UX designers continues to grow as companies realize that great design drives customer loyalty and business success. Many people aspire to become UX designers, but the role requires a diverse set of skills that go far beyond visual design.
To succeed in this field, you must understand users, communicate effectively, and bring ideas to life through thoughtful design decisions. Below is a list of essential skills every aspiring user experience designer should develop.
1. Sketching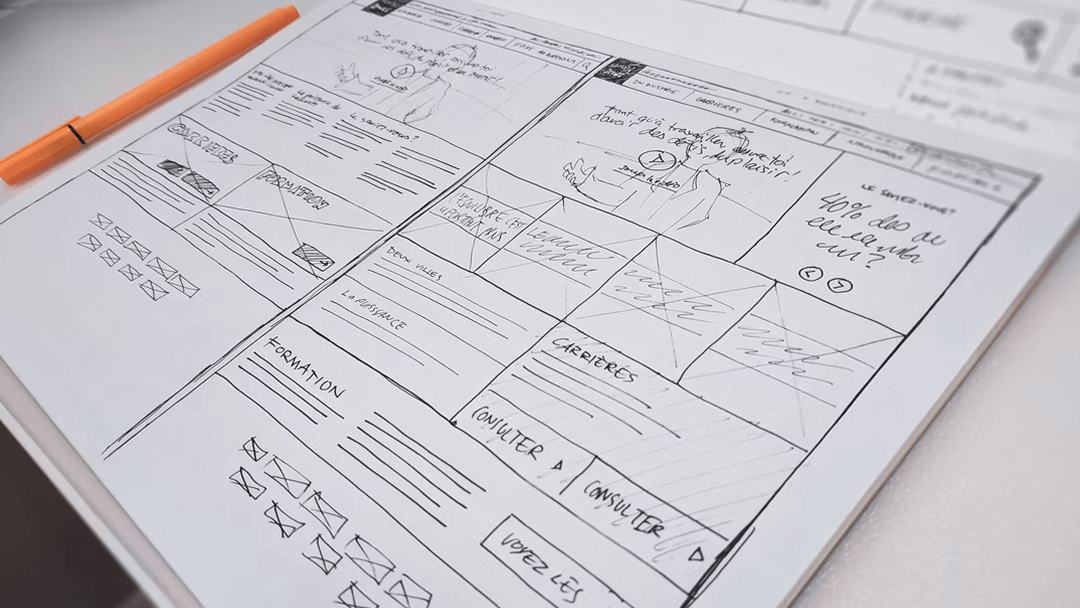
Sketching is one of the most fundamental skills for any UX designer. It helps you quickly capture ideas and explore concepts before diving into digital tools. By sketching wireframes or layouts on paper or a whiteboard, you can focus on structure and flow without getting lost in design details.
It also plays a key role in collaboration. Sharing quick sketches with teammates or stakeholders makes it easier to discuss ideas, gather feedback, and refine solutions early in the design process.
2. User Research
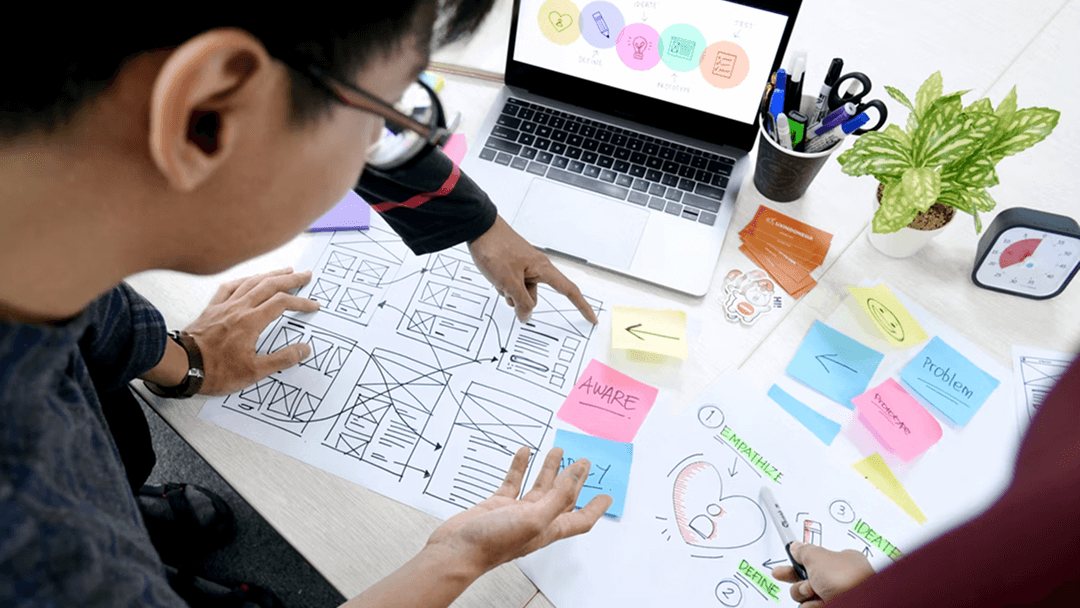
Understanding the user is the foundation of UX design. User research allows you to learn who your users are, what they need, and how they interact with your product. This process can involve interviews, surveys, usability tests, and observation.
A strong UX designer knows how to select the right research methods for each project and synthesize the findings into actionable insights. The goal is to build empathy for users and use real data to inform design decisions.
3. Content Strategy
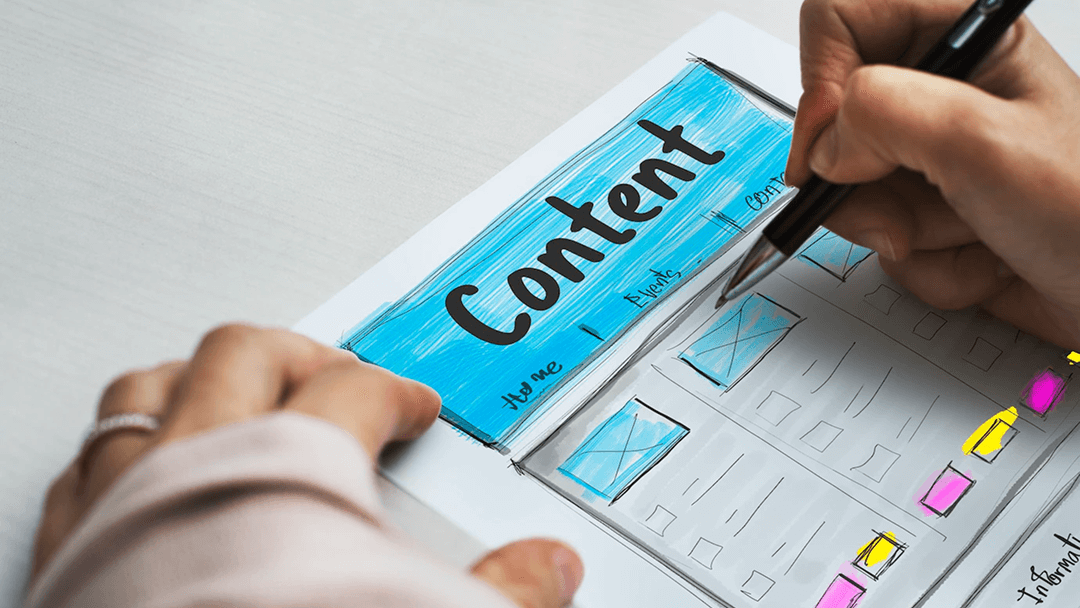
Content is at the heart of every experience. A well-defined content strategy ensures that your message is clear, relevant, and useful. UX designers must understand how content supports user goals, whether it’s through microcopy, headlines, or navigation labels.
Consistency across all touchpoints is key. Designers who understand both content and design can create smoother, more cohesive experiences that connect with users on a deeper level.
4. Wireframing
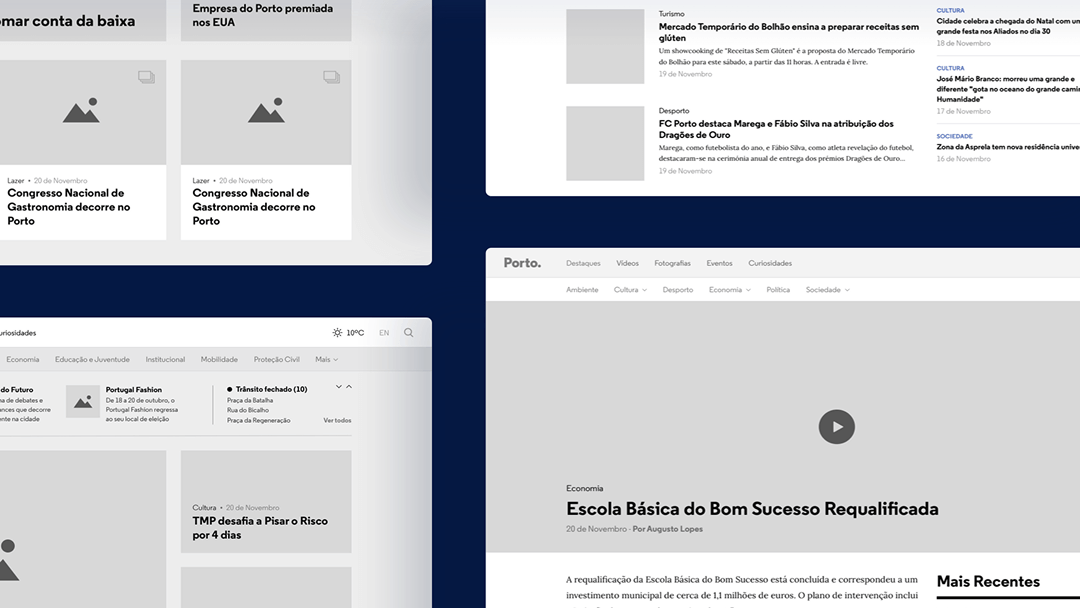
Wireframing is the process of mapping out the structure and flow of a product. It’s a visual blueprint that outlines where content, buttons, and navigation will appear. Wireframes help teams focus on functionality and usability before jumping into detailed design.
This skill is crucial because it bridges the gap between ideas and real products. A good wireframe clarifies user journeys, highlights potential issues, and ensures everyone shares the same vision before development begins.
5. Information Architecture
Information Architecture (IA) is about organizing content in a way that makes sense to users. It ensures that information is easy to find, intuitive to navigate, and logically structured. Effective IA prevents confusion and enhances the user’s ability to complete tasks efficiently.
As a UX designer, you’ll often create site maps, flow diagrams, and navigation systems that define how users move through an interface. Clear structure builds confidence and improves the overall experience.
6. Visual Design and Design Tools
While UX focuses on experience, a strong sense of visual design is still essential. UX designers often create wireframes, prototypes, and high-fidelity mockups to bring concepts to life. This requires proficiency in tools such as Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD.
Additionally, understanding principles like typography, spacing, and color harmony helps create visually appealing and consistent designs. Familiarity with motion design tools such as After Effects can also be valuable for creating interactive prototypes.
7. UX Writing

Words are a vital part of design. UX writing focuses on crafting clear, concise, and helpful text that guides users through an experience. From button labels to onboarding messages, every word should make the interface easier to use.
Strong writing skills also help you communicate design ideas, create user stories, and collaborate effectively with developers and content teams. Good UX writing turns functionality into a user-friendly, human experience.
8. Communication and Presentation

Great design only succeeds when others understand and support it. UX designers must communicate ideas clearly, listen to feedback, and present their work confidently to stakeholders or clients.
Whether you’re leading a workshop, presenting a prototype, or explaining research findings, communication and presentation skills help you gain buy-in and ensure that your vision is properly implemented.
9. Interaction Design
Interaction design (IxD) focuses on how users engage with a product’s interface. It’s about designing smooth, intuitive interactions that make tasks effortless. This includes everything from button behavior and transitions to overall user flow.
A successful UX designer anticipates user behavior, identifies friction points, and designs solutions that feel natural. Understanding common usability patterns and accessibility standards helps ensure that every interaction is both functional and delightful.
UX Design vs. UI Design
UX and UI are closely related but not the same.
- UX Design focuses on the overall experience — structure, flow, and functionality.
- UI Design focuses on the visual elements — colors, typography, and layouts.
Think of UX as the blueprint and UI as the paint and decor. A successful product needs both to feel complete and enjoyable.
Examples of Good UX Design
- Spotify: Personalized playlists and smooth navigation make music discovery effortless.
- Airbnb: Clear booking steps and trusted user feedback build confidence.
- Apple: Simple interactions and consistent interfaces create an intuitive ecosystem.
Each of these companies prioritizes ease of use, feedback, and emotional connection — the core of great UX.
The Future of UX Design
As technology evolves, UX continues to expand beyond screens. Voice interfaces, AI-driven personalization, and immersive experiences are shaping the next generation of digital design. Yet, the foundation remains the same — understanding human needs and designing around them.
Conclusion
UX design is about empathy, simplicity, and purpose. It connects human behavior with digital innovation, ensuring that technology serves people rather than the other way around. Whether you are a beginner learning the basics or a designer refining your craft, understanding UX principles is key to creating products people love to use.