How to Create a User-Friendly User Interface? A Beginner's Guide

Creating a user-friendly interface is one of the most crucial aspects of designing an application, website, or software. Without an intuitive UI (User Interface), users may struggle to navigate your product, leading to frustration and abandonment.
No one wants to waste time figuring out how to use a website or software. In this guide, we will teach you the basics of user interface design, from understanding your user base to crafting an intuitive layout. Follow these best practices to create a seamless and visually appealing interface that enhances user experience.
What is a User Interface?
The goal of user interface (UI) design is to ensure smooth and efficient interaction between users and a system. A well-designed UI simplifies navigation, enhances usability, and improves user satisfaction.
Effective UI design integrates graphic design, typography, and layout principles to optimize functionality while ensuring an aesthetically pleasing experience. The best interfaces remain unobtrusive, allowing users to focus on their tasks with minimal effort.
Other types of user interfaces can include:
Form-based user interface: Form-based user interface is used to enter data into a program or application Some forms may offer a limited selection of choices, and others may be designed for more complex inputs—like social security numbers or bank account information.
Graphical user interface: The graphical user interface (GUI) is the most commonly used today. It relies on graphical icons and symbols that the user can interact with. This type of interface is mostly used with personal computers, tablets, and smartphones. The GUI was first developed at the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center in the early 1970s.
Menu-driven user interface: A menu-driven user interface is a type of user interface that relies on menus to allow users to interact with the system. This type of interface is often found in software applications and systems, where users can select and execute commands from a menu. Menu-driven interfaces are often considered easier to use than other types of interfaces, as users can simply navigate through the menus to find the command they need.
Voice user interface: It’s a technology that allows humans to interact with computers and devices using only their voice. This could be through a dedicated microphone or simply by talking into the device’s mic. VUI has been around for a while, but it’s becoming increasingly popular with the advent of voice-activated assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
User interface design is a process of using graphical or text elements to create a screen or screens that allow a user to interact with a system. By understanding the user interface, you can create an effective design that makes it easy for users to interact with your system and complete the task they are trying to achieve.
What are the Principles of a User-Friendly Interface?
In the digital age, when so many aspects of our lives are conducted online, user interface (UI) design has become increasingly important. While most people are probably familiar with what user interface design is, few understand the basic principles that make it effective.
Now, we will explore the five basic principles of user interface design and show how they can be applied to create a more user-friendly online experience
Visual Clarity
The most important principle for user interface design is clarity. When designing an interface, you must take into account the user's needs and make sure that all elements of the interface are easy to understand and use. Every button, icon, and text element should be self-explanatory, and users should be able to complete tasks without difficulty. Clarity is essential for creating a positive user experience, and ensuring that users can interact with your interface in the way that you intend.
Consistency
A consistent user interface (UI) is key to a positive user experience. When users know what to expect from your product, they're able to focus on their task rather than trying to figure out how the product works. This is why it's important to apply the same design principles to all elements of your UI. Users should be able to understand an element's function by its appearance alone, without needing to refer to a tutorial or manual.
Additionally, consistency helps build trust between your product and your users. When users know that they can depend on your product to behave in a certain way, they're more likely to stick around and become loyal customers.
User Control
To ensure an intuitive user experience, it's important to allow users to control their interactions with your product. This means giving them clear and concise controls that are easy to understand and easy to use. Placing these controls in logical locations is also key, as is making sure they're visually consistent with the overall design of your product. It's also important to allow users to undo actions if they make a mistake, or if they simply change their minds. Allowing users to take charge of their interactions with your product will help them feel in control and confident while using it.
Hierarchy
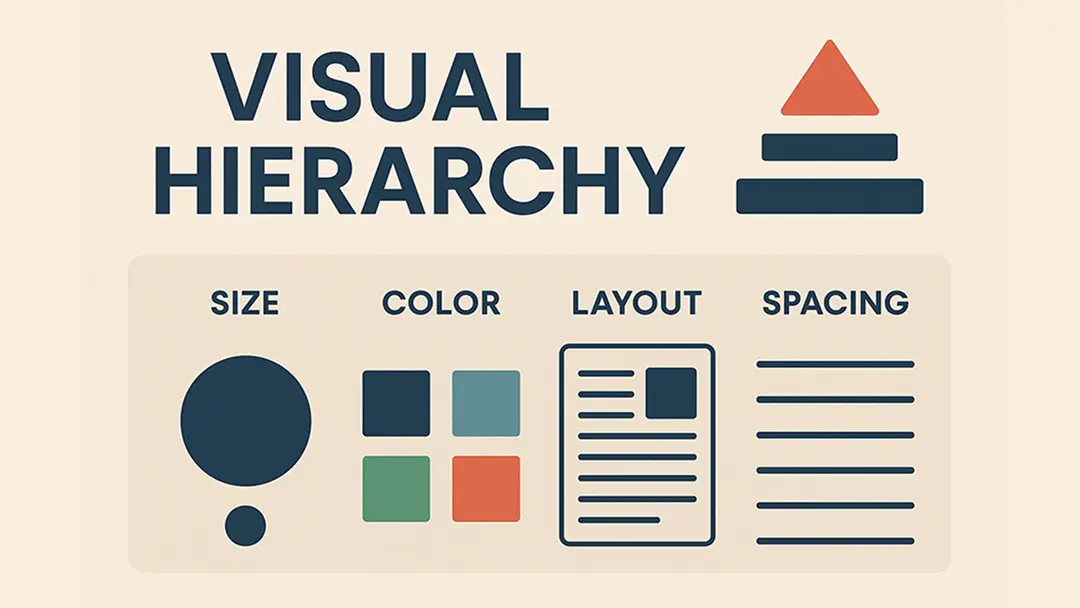
Hierarchy is another key principle in UI design. This is the order in which different elements on the screen are arranged and it helps to guide the user's eye to the most important information. Important items should be at the top of the screen and less important ones towards the bottom. You can also use hierarchy to create visual groups of related items, making it easy for users to scan and find what they're looking for.
Negative space
Have you ever wondered why certain elements on a screen are designed in a certain way? Chances are, it's due to something called negative space. Negative space is the empty or unused space around and between the elements of a composition. It's an important design principle because it can be used to create balance and order.
When used correctly, negative space can make a design more visually pleasing and easier to use. So how do you use it? Just think about the space between text and graphics, or between different elements on the screen. You can also use it to create focal points and guide the user's eye toward certain areas. For example, our login button is intentionally designed to stand out against the background. By using negative space, we're able to create a more visually appealing and user-friendly interface.
How to Design a User-Friendly Interface?
1. Know Your Users
Conduct user research to understand your audience’s preferences, pain points, and behavior. This helps tailor the UI to meet user needs effectively.
2. Keep It Simple and Intuitive
A cluttered UI confuses users. Stick to a minimalist approach, ensuring that essential functions are easily accessible.
3. Optimize for Different Devices
Your UI should be responsive and optimized for desktop, mobile, and tablet experiences. Consistent performance across devices improves accessibility.
4. Use High-Contrast and Readable Fonts
Readable typography and high-contrast elements enhance accessibility and legibility, making the UI user-friendly for all audiences.
5. Provide Clear Feedback
Use visual indicators, tooltips, and animations to guide users and confirm actions. Instant feedback enhances user confidence and prevents errors.
Testing Your User Interface
As you build your user interface, it's important to test it out. This means clicking and scrolling through all the pages and menus to make sure everything works properly. You might also want to try out different user scenarios to see how the interface behaves. For example, what happens if a user enters incorrect information? Or tries to navigate to a page that doesn't exist? By testing your UI, you can catch any potential glitches and fix them before your users do.
To better understand what users need and how to meet those needs, you can explore some of the best examples of user needs for inspiration and guidance.
Final Words
Creating a user-friendly UI is essential for enhancing engagement, retention, and conversions. By applying these principles and continuously optimizing based on user feedback and testing, you can design interfaces that users will love.
Remember: A great UI is not just about aesthetics—it’s about usability, accessibility, and efficiency. Implement these best practices, and you’ll build an interface that truly enhances the user experience.